THE PROBLEM:
The majority of children living in poor rural or urban communities in India have access to inadequate schooling options. Schools are characterized by the high child-teacher ratio (1:50), use of rote method (including corporal punishment), poor infrastructure, high drop-out rates and no extra-curricular activities. Teachers are often underpaid, untrained, and not motivated to teach. This undermines children’s potential to learn and challenge the socio-economic conditions they are born into.
School Program
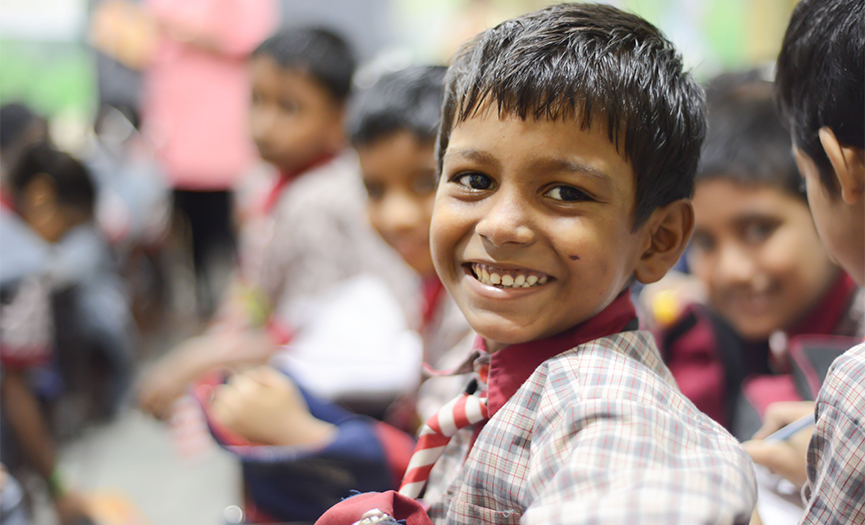

School Program
-

Location
Dharavi
-

Type of Beneficary
Child
-

BENEFICIARY AGE
3-10
-
ANNUAL MEMBERS
450
OUR SOLUTION:
By working with youth from Dharavi who went to substandard schools Reality Gives collected first-hand information on how negatively this impacted their future career and education opportunities. To tackle the issue, we joined hands with a low-income school with the goal is to develop a model school in the heart of the slum where children can achieve their full potential regardless of their circumstances.
OUR BENEFICIARIES:
Our 440 children are at the heart of what we do at school and our focus is to ensure they become independent learners and can choose their life path. The program also is a rare opportunity for employment and empowerment in an area where gender inequality is still widespread, as all the teachers are women hired from Dharavi and trained by our education experts to become “Champion teachers”. Last but not the least, working at the school allow us to engage and support the parents’ community at large.
OUR PROGRAM:
In 2013 we started our School Program in Dharavi, now delivering English medium holistic education to 440 students Nursery to Grade 4. We hired qualified school leaders and a higher number of teachers introduced an “academic values mindsets” education approach and extracurricular activities such as art, IT, music, and exposure visits. We deploy regular Teacher Training and development workshops for the parents’ community. Through these activities, we are observing a positive change in the students’ learning outcomes and attendance.

Academics
Academic knowledge of core subjects including literacy and mathematics are needed to succeed in school and the work environment.

Values
The underlying beliefs and mindsets that determine our actions and how we make different choices in our lives.
Exposure
Knowledge and skills that are outside the scope of our daily lives; which help us identify our aspirations and how to get there.
SUCCESS STORIES
We are committed to help our children and teachers. Their stories tell us that through equitable access to education and development opportunities change is possible.
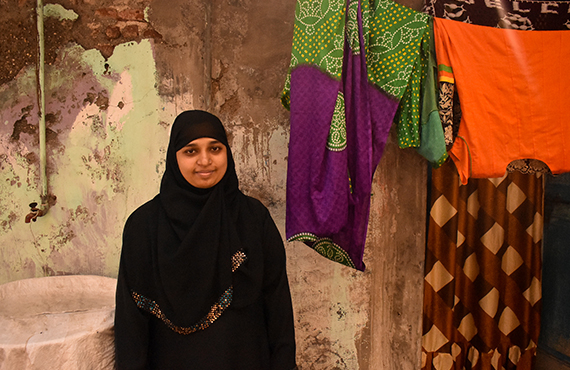
ASMA

KISHAN

HITEN

KOMAL
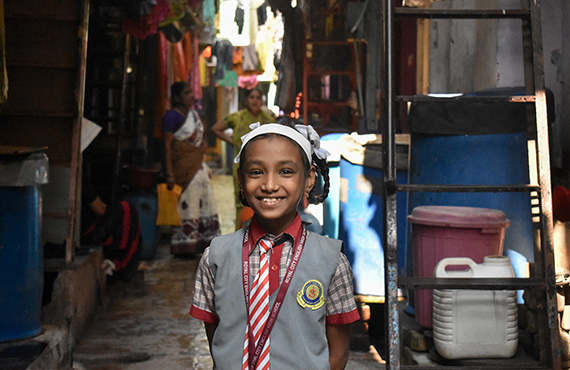
SONAKSHI
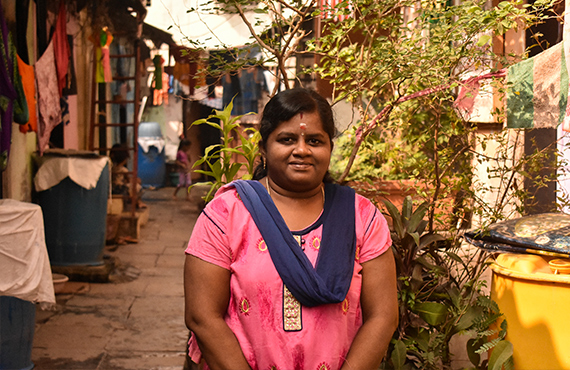
SUJATHA
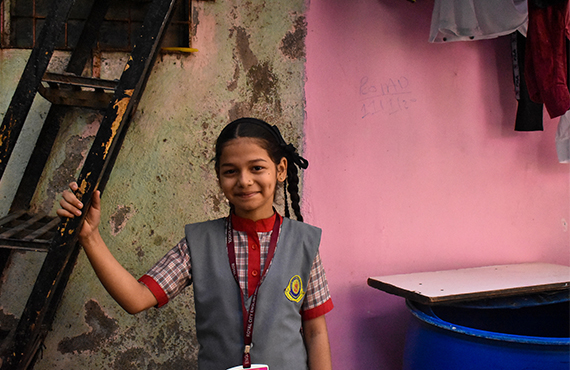
HEENA
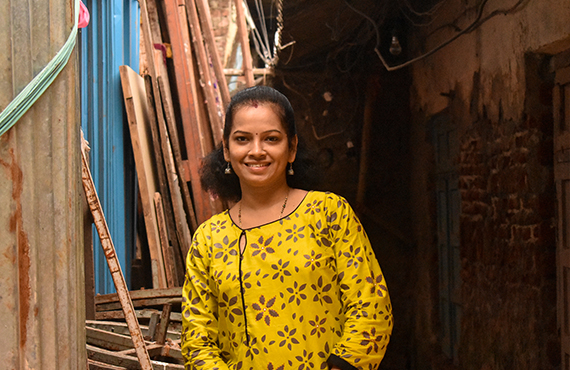
MALIKA
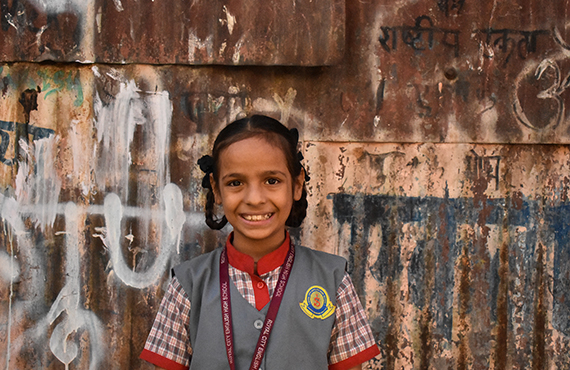
TANZIL
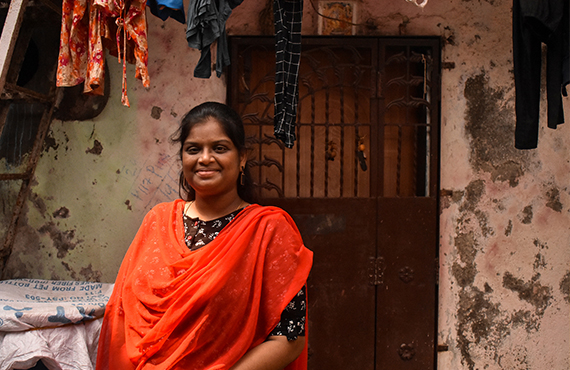
ANITHA
Our Program Partners
Donation Options
-
 1 YEAR - 1 TEACHER SALARY$ 2500 | € 2,290 | ₹ 190,000
1 YEAR - 1 TEACHER SALARY$ 2500 | € 2,290 | ₹ 190,000 -
 1 MONTH - STATIONERY & LEARNING TOOLS$ 300 | € 290 | ₹ 23,750
1 MONTH - STATIONERY & LEARNING TOOLS$ 300 | € 290 | ₹ 23,750 -
 1 YEAR - NOTEBOOK SUPPLY$ 125 | € 115 | ₹ 9,500
1 YEAR - NOTEBOOK SUPPLY$ 125 | € 115 | ₹ 9,500
DONATE
Your donation will help give youth and children from urban slums access to quality education, a safe learning environment and a second chance in life.
Donate